Forward modeling synthetic seismograms and displacements¶
Calculate synthetic seismograms from a local GF store¶
It is assumed that a Store with store ID crust2_dd has been downloaded in advance. A list of currently available stores can be found at https://greens-mill.pyrocko.org as well as how to download such stores.
Further API documentation for the utilized objects can be found at Target, LocalEngine and DCSource.
Download gf_forward_example1.py
import os
from pyrocko.gf import LocalEngine, Target, DCSource, ws
from pyrocko import trace
from pyrocko.marker import PhaseMarker
# The store we are going extract data from:
store_id = 'iceland_reg_v2'
# First, download a Greens Functions store. If you already have one that you
# would like to use, you can skip this step and point the *store_superdirs* in
# the next step to that directory.
if not os.path.exists(store_id):
ws.download_gf_store(site='kinherd', store_id=store_id)
# We need a pyrocko.gf.Engine object which provides us with the traces
# extracted from the store. In this case we are going to use a local
# engine since we are going to query a local store.
engine = LocalEngine(store_superdirs=['.'])
# Define a list of pyrocko.gf.Target objects, representing the recording
# devices. In this case one station with a three component sensor will
# serve fine for demonstation.
channel_codes = 'ENZ'
targets = [
Target(
lat=10.,
lon=10.,
store_id=store_id,
codes=('', 'STA', '', channel_code))
for channel_code in channel_codes]
# Let's use a double couple source representation.
source_dc = DCSource(
lat=11.,
lon=11.,
depth=10000.,
strike=20.,
dip=40.,
rake=60.,
magnitude=4.)
# Processing that data will return a pyrocko.gf.Reponse object.
response = engine.process(source_dc, targets)
# This will return a list of the requested traces:
synthetic_traces = response.pyrocko_traces()
# In addition to that it is also possible to extract interpolated travel times
# of phases which have been defined in the store's config file.
store = engine.get_store(store_id)
markers = []
for t in targets:
dist = t.distance_to(source_dc)
depth = source_dc.depth
arrival_time = store.t('begin', (depth, dist))
m = PhaseMarker(tmin=arrival_time,
tmax=arrival_time,
phasename='P',
nslc_ids=(t.codes,))
markers.append(m)
# Finally, let's scrutinize these traces.
trace.snuffle(synthetic_traces, markers=markers)
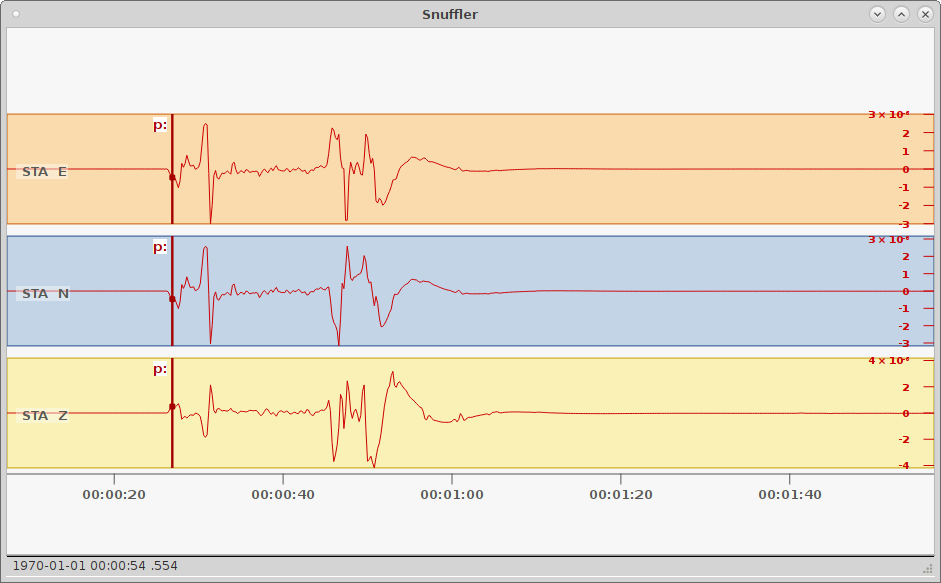
Synthetic seismograms calculated through pyrocko.gf displayed in Snuffler - seismogram browser and workbench. The three traces show the east, north and vertical synthetical displacement stimulated by a double-couple source at 155 km distance.
Calculate spatial surface displacement from a local GF store¶
In this example we create a RectangularSource and compute the spatial static displacement invoked by that rupture.
We will utilize LocalEngine, StaticTarget and SatelliteTarget.
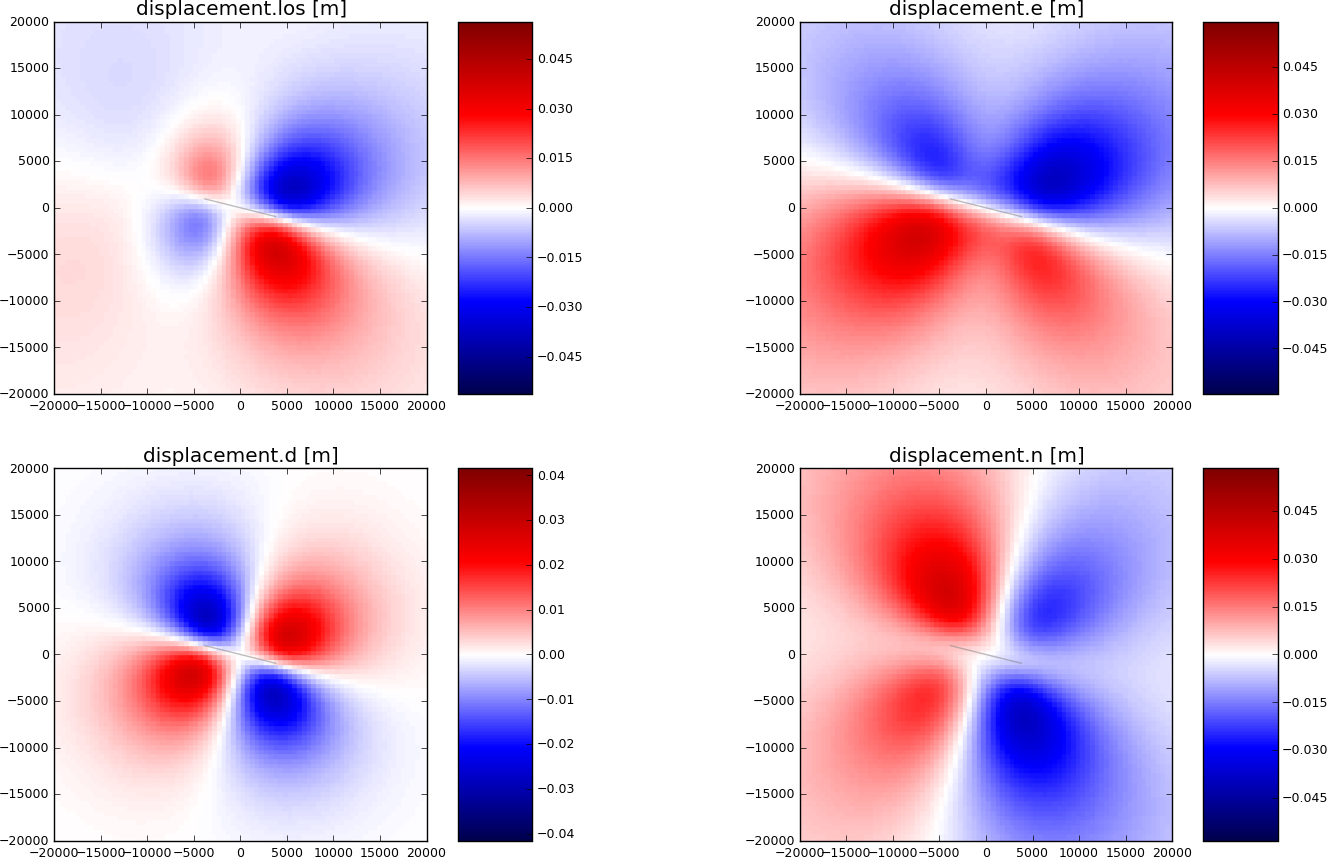
Synthetic surface displacement from a vertical strike-slip fault, with a N104W azimuth, in the Line-of-sight (LOS), east, north and vertical directions. LOS as for Envisat satellite (Look Angle: 23., Heading:-76). Positive motion toward the satellite.
Download gf_forward_example2.py
import os.path
from pyrocko import gf
import numpy as num
# Download a Greens Functions store, programmatically.
store_id = 'gf_abruzzo_nearfield_vmod_Ameri'
if not os.path.exists(store_id):
gf.ws.download_gf_store(site='kinherd', store_id=store_id)
# Setup the LocalEngine and point it to the fomosto store you just downloaded.
# *store_superdirs* is a list of directories where to look for GF Stores.
engine = gf.LocalEngine(store_superdirs=['.'])
# We define an extended source, in this case a rectangular geometry
# Centroid UTM position is defined relatively to geographical lat, lon position
# Purely lef-lateral strike-slip fault with an N104W azimuth.
km = 1e3 # for convenience
rect_source = gf.RectangularSource(
lat=0., lon=0.,
north_shift=0., east_shift=0., depth=6.5*km,
width=5*km, length=8*km,
dip=90., rake=0., strike=104.,
slip=1.)
# We will define a grid of targets
# number in east and north directions, and total
ngrid = 80
# extension from origin in all directions
obs_size = 20.*km
ntargets = ngrid**2
# make regular line vector
norths = num.linspace(-obs_size, obs_size, ngrid)
easts = num.linspace(-obs_size, obs_size, ngrid)
# make regular grid
norths2d = num.repeat(norths, len(easts))
easts2d = num.tile(easts, len(norths))
# We initialize the satellite target and set the line of sight vectors
# direction, example of the Envisat satellite
look = 23. # angle between the LOS and the vertical
heading = -76 # angle between the azimuth and the east (anti-clock)
theta = num.empty(ntargets) # vertical LOS from horizontal
theta.fill(num.deg2rad(90. - look))
phi = num.empty(ntargets) # horizontal LOS from E in anti-clokwise rotation
phi.fill(num.deg2rad(-90-heading))
satellite_target = gf.SatelliteTarget(
north_shifts=norths2d,
east_shifts=easts2d,
tsnapshot=24. * 3600., # one day
interpolation='nearest_neighbor',
phi=phi,
theta=theta,
store_id=store_id)
# The computation is performed by calling process on the engine
result = engine.process(rect_source, [satellite_target])
def plot_static_los_result(result, target=0):
'''Helper function for plotting the displacement'''
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# get target coordinates and displacements from results
N = result.request.targets[target].coords5[:, 2]
E = result.request.targets[target].coords5[:, 3]
synth_disp = result.results_list[0][target].result
# get the component names of displacements
components = synth_disp.keys()
fig, _ = plt.subplots(int(len(components)/2), int(len(components)/2))
vranges = [(synth_disp[k].max(),
synth_disp[k].min()) for k in components]
for comp, ax, vrange in zip(components, fig.axes, vranges):
lmax = num.abs([num.min(vrange), num.max(vrange)]).max()
# plot displacements at targets as colored points
cmap = ax.scatter(E, N, c=synth_disp[comp], s=10., marker='s',
edgecolor='face', cmap='seismic',
vmin=-1.5*lmax, vmax=1.5*lmax)
ax.set_title(comp+' [m]')
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.set_xlim(-obs_size, obs_size)
ax.set_ylim(-obs_size, obs_size)
# We plot the modeled fault
n, e = rect_source.outline(cs='xy').T
ax.fill(e, n, color=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5), alpha=0.5)
fig.colorbar(cmap, ax=ax, aspect=5)
plt.show()
plot_static_los_result(result)
Calculate spatial surface displacement using subfault dislocations¶
In this example we create a OkadaSource and compute the spatial static displacement at the surface invoked by that rupture [1].
Download okada_forward_example.py
import numpy as num
from pyrocko.modelling import OkadaSource, okada_ext
from pyrocko.plot import dislocation as displt
d2r = num.pi / 180.
km = 1000.
# Set source parameter
src_north, src_east, src_depth = 0. * km, 0. * km, 100. * km
length_total = 50. * km
width_total = 15. * km
nlength = 50
nwidth = 15
al1 = -length_total / 2.
al2 = length_total / 2.
aw1 = -width_total / 2.
aw2 = width_total / 2.
# Define rupture plane and discretize it depending on nlength, nwidth
source = OkadaSource(
lat=0., lon=0., north_shift=src_north, east_shift=src_east,
depth=src_depth,
al1=al1, al2=al2, aw1=aw1, aw2=aw2,
strike=45., dip=90., rake=90.,
slip=1., opening=0., poisson=0.25, shearmod=32.0e9)
source_discretized, _ = source.discretize(nlength, nwidth)
# Set receiver at the surface
receiver_coords = num.zeros((10000, 3))
margin = length_total * 3
receiver_coords[:, 0] = \
num.tile(num.linspace(-margin, margin, 100), 100) + src_north
receiver_coords[:, 1] = \
num.repeat(num.linspace(-margin, margin, 100), 100) + src_east
# Calculation of displacements due to source at receiver_coords points
source_patch = num.array([
patch.source_patch() for patch in source_discretized])
source_disl = num.array([
patch.source_disloc() for patch in source_discretized])
result = okada_ext.okada(
source_patch, source_disl, receiver_coords,
source.lamb, source.shearmod, 0)
# Plot
displt.plot(result, receiver_coords, cmap='coolwarm', zero_center=True)
Footnotes
| [1] | Okada, Y., Gravity and potential changes due to shear and tensile faults in a half-space. In: Journal of Geophysical Research 82.2, 1018–1040. doi:10.1029/92JB00178, 1992. |
Calculate spatial surface displacement and export Kite scenes¶
We derive InSAR surface deformation targets from Kite scenes. This way we can easily inspect the data and use Kite’s quadtree data sub-sampling and data error variance-covariance estimation calculation.
Download gf_forward_example2_kite.py
import os.path
from kite.scene import Scene, FrameConfig
from pyrocko import gf
import numpy as num
km = 1e3
d2r = num.pi/180.
# Download a Greens Functions store
store_id = 'gf_abruzzo_nearfield_vmod_Ameri'
if not os.path.exists(store_id):
gf.ws.download_gf_store(site='kinherd', store_id=store_id)
# Setup the modelling LocalEngine
# *store_superdirs* is a list of directories where to look for GF Stores.
engine = gf.LocalEngine(store_superdirs=['.'])
rect_source = gf.RectangularSource(
# Geographical position [deg]
lat=0., lon=0.,
# Relative cartesian offsets [m]
north_shift=10*km, east_shift=10*km,
depth=6.5*km,
# Dimensions of the fault [m]
width=5*km, length=8*km,
strike=104., dip=90., rake=0.,
# Slip in [m]
slip=1., anchor='top')
# Define the scene's frame
frame = FrameConfig(
# Lower left geographical reference [deg]
llLat=0., llLon=0.,
# Pixel spacing [m] or [degrees]
spacing='meter', dE=250, dN=250)
# Resolution of the scene
npx_east = 800
npx_north = 800
# 2D arrays for displacement and look vector
displacement = num.empty((npx_east, npx_north))
# Look vectors
# Theta is elevation angle from horizon
theta = num.full_like(displacement, 48.*d2r)
# Phi is azimuth towards the satellite, counter-clockwise from East
phi = num.full_like(displacement, 23.*d2r)
scene = Scene(
displacement=displacement,
phi=phi, theta=theta,
frame=frame)
# Or just load an existing scene!
# scene = Scene.load('my_scene_asc.npy')
satellite_target = gf.KiteSceneTarget(
scene,
store_id=store_id)
# Forward model!
result = engine.process(
rect_source, satellite_target,
# Use all available cores
nthreads=0)
kite_scenes = result.kite_scenes()
# Show the synthetic data in spool
# kite_scenes[0].spool()
Calculate forward model of thrust faulting and display wrapped phase¶
In this example we compare the synthetic unwappred and wrapped LOS displacements caused by a thrust rupture.
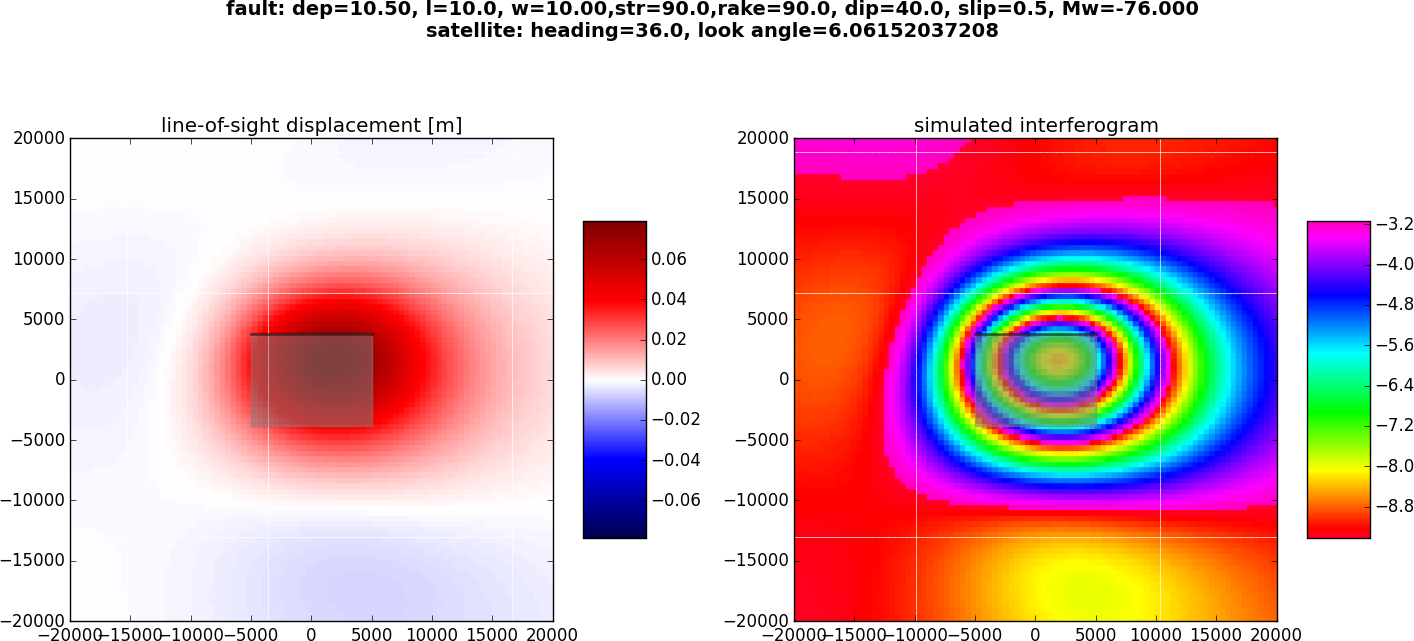
Synthetic LOS displacements from a south-dipping thrust fault. LOS as for Sentinel-1 satellite (Look Angle: 36., Heading:-76). Positive motion toward the satellite. Left: unwrapped phase. Right: Wrapped phase.
Download gf_forward_example3.py
import os.path
import numpy as num
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pyrocko import gf
km = 1e3
# Download a Greens Functions store, programmatically.
store_id = 'gf_abruzzo_nearfield_vmod_Ameri'
if not os.path.exists(store_id):
gf.ws.download_gf_store(site='kinherd', store_id=store_id)
# Ignite the LocalEngine and point it to your fomosto store at '.'
engine = gf.LocalEngine(store_superdirs=['.'])
# RectangularSource parameters
strike = 90.
dip = 40.
dep = 10.5*km
leng = 10.*km
wid = 10.*km
rake = 90.
slip = .5
# Magnitude of the event
potency = leng * wid * slip
rigidity = 31.5e9
m0 = potency*rigidity
mw = (2./3) * num.log10(m0) - 6.07
# Define an extended RectangularSource
thrust = gf.RectangularSource(
north_shift=0., east_shift=0.,
depth=dep, width=wid, length=leng,
dip=dip, rake=rake, strike=strike,
slip=slip)
# Define a grid of targets
# number in east and north directions, and total
ngrid = 40
# ngrid = 90 # for better resolution
# extension from origin in all directions
obs_size = 20.*km
ntargets = ngrid**2
norths = num.linspace(-obs_size, obs_size, ngrid)
easts = num.linspace(-obs_size, obs_size, ngrid)
# make regular grid
norths2d = num.repeat(norths, len(easts))
easts2d = num.tile(easts, len(norths))
# Initialize the SatelliteTarget and set the line of site vectors
# Case example of the Sentinel-1 satellite:
#
# Heading: -166 (anti-clockwise rotation from east)
# Average Look Angle: 36 (from vertical)
heading = -76.
look = 36.
phi = num.empty(ntargets) # Horizontal LOS from E in anti-clockwise rotation
theta = num.empty(ntargets) # Vertical LOS from horizontal
phi.fill(num.deg2rad(-90-heading))
theta.fill(num.deg2rad(90.-look))
satellite_target = gf.SatelliteTarget(
north_shifts=norths2d,
east_shifts=easts2d,
tsnapshot=24.*3600., # one day
interpolation='nearest_neighbor',
phi=phi,
theta=theta,
store_id=store_id)
# Forward-modell is performed by calling 'process' on the engine
result = engine.process(thrust, [satellite_target])
# Retrieve synthetic displacements and coordinates from engine's result
# of the first target (it=0)
it = 0
N = result.request.targets[it].coords5[:, 2]
E = result.request.targets[it].coords5[:, 3]
synth_disp = result.results_list[0][it].result
# Fault projection to the surface for plotting
n, e = thrust.outline(cs='xy').T
fig, _ = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(8, 4))
fig.suptitle(
"fault: dep={:0.2f}, l={}, w={:0.2f},str={},"
"rake={}, dip={}, slip={}, Mw={:0.3f}\n"
"satellite: heading={}, look angle={}"
.format(dep/km, leng/km, wid/km,
strike, rake, dip, slip, heading, look, mw),
fontsize=14,
fontweight='bold')
# Shift the relative LOS displacements
los = synth_disp['displacement.los']
losrange = [(los.max(), los.min())]
losmax = num.abs([num.min(losrange), num.max(losrange)]).max()
# Plot unwrapped LOS displacements
ax = fig.axes[0]
cmap = ax.scatter(
E, N, c=los,
s=10., marker='s',
edgecolor='face',
cmap=plt.get_cmap('seismic'),
vmin=-1.*losmax, vmax=1.*losmax)
ax.set_title('line-of-sight displacement [m]')
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.set_xlim(-obs_size, obs_size)
ax.set_ylim(-obs_size, obs_size)
# Fault outline
ax.fill(e, n, color=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5), alpha=0.5)
# Underline the tip of the thrust
ax.plot(e[:2], n[:2], linewidth=2., color='black', alpha=0.5)
fig.colorbar(cmap, ax=ax, orientation='vertical', aspect=5, shrink=0.5)
# Simulate a C-band interferogram for this source
c_lambda = 0.056
insar_phase = -num.mod(los, c_lambda/2.)/(c_lambda/2.)*2.*num.pi - num.pi
# Plot wrapped phase
ax = fig.axes[1]
cmap = ax.scatter(
E, N, c=insar_phase,
s=10., marker='s',
edgecolor='face',
cmap=plt.get_cmap('gist_rainbow'))
ax.set_xlim(-obs_size, obs_size)
ax.set_ylim(-obs_size, obs_size)
ax.set_title('simulated interferogram')
ax.set_aspect('equal')
# plot fault outline
ax.fill(e, n, color=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5), alpha=0.5)
# We outline the top edge of the fault with a thick line
ax.plot(e[:2], n[:2], linewidth=2., color='black', alpha=0.5)
fig.colorbar(cmap, orientation='vertical', shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
plt.show()
Combining dislocation sources¶
In this example we combine two rectangular sources and plot the forward model in profile.
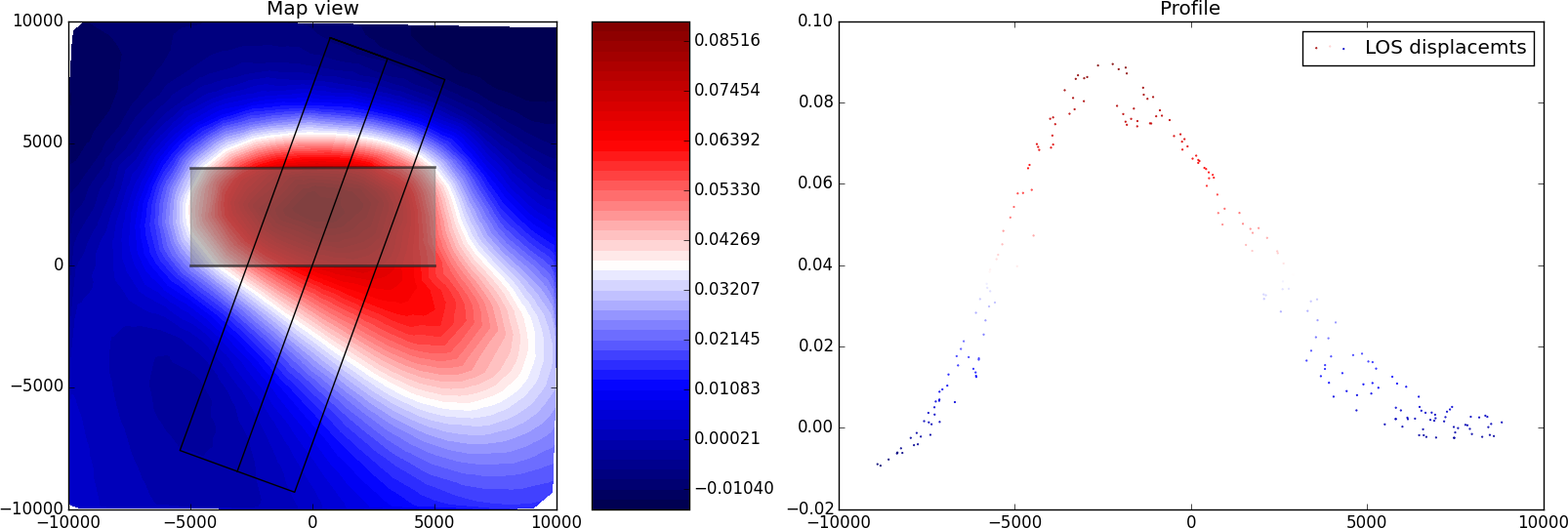
Synthetic LOS displacements from a flower-structure made of one strike-slip fault and one thrust fault. LOS as for Sentinel-1 satellite (Look Angle: 36°, Heading: -76°). Positive motion toward the satellite.
Download gf_forward_example4.py
import os.path
import numpy as num
from pyrocko import gf
from pyrocko.guts import List
class CombiSource(gf.Source):
'''Composite source model.'''
discretized_source_class = gf.DiscretizedMTSource
subsources = List.T(gf.Source.T())
def __init__(self, subsources=[], **kwargs):
if subsources:
lats = num.array(
[subsource.lat for subsource in subsources], dtype=num.float)
lons = num.array(
[subsource.lon for subsource in subsources], dtype=num.float)
assert num.all(lats == lats[0]) and num.all(lons == lons[0])
lat, lon = lats[0], lons[0]
# if not same use:
# lat, lon = center_latlon(subsources)
depth = float(num.mean([p.depth for p in subsources]))
t = float(num.mean([p.time for p in subsources]))
kwargs.update(time=t, lat=float(lat), lon=float(lon), depth=depth)
gf.Source.__init__(self, subsources=subsources, **kwargs)
def get_factor(self):
return 1.0
def discretize_basesource(self, store, target=None):
dsources = []
t0 = self.subsources[0].time
for sf in self.subsources:
assert t0 == sf.time
ds = sf.discretize_basesource(store, target)
ds.m6s *= sf.get_factor()
dsources.append(ds)
return gf.DiscretizedMTSource.combine(dsources)
# Download a Greens Functions store, programmatically.
store_id = 'gf_abruzzo_nearfield_vmod_Ameri'
if not os.path.exists(store_id):
gf.ws.download_gf_store(site='kinherd', store_id=store_id)
km = 1e3 # distance in kilometer
# We define a grid for the targets.
left, right, bottom, top = -10*km, 10*km, -10*km, 10*km
ntargets = 1000
# Ignite the LocalEngine and point it to fomosto stores stored on a
# USB stick, for this example we use a static store with id 'static_store'
engine = gf.LocalEngine(store_superdirs=['.'])
store_id = 'gf_abruzzo_nearfield_vmod_Ameri'
# We define two finite sources
# The first one is a purely vertical strike-slip fault
strikeslip = gf.RectangularSource(
north_shift=0., east_shift=0.,
depth=6*km, width=4*km, length=10*km,
dip=90., rake=0., strike=90.,
slip=1.)
# The second one is a ramp connecting to the root of the strike-slip fault
# ramp north shift (n) and width (w) depend on its dip angle and on
# the strike slip fault width
n, w = 2/num.tan(num.deg2rad(45.)), 2.*(2./(num.sin(num.deg2rad(45.))))
thrust = gf.RectangularSource(
north_shift=n*km, east_shift=0.,
depth=6*km, width=w*km, length=10*km,
dip=45., rake=90., strike=90.,
slip=0.5)
# We initialize the satellite target and set the line of site vectors
# Case example of the Sentinel-1 satellite:
# Heading: -166 (anti clockwise rotation from east)
# Average Look Angle: 36 (from vertical)
heading = -76
look = 36.
phi = num.empty(ntargets) # Horizontal LOS from E in anti-clockwise rotation
theta = num.empty(ntargets) # Vertical LOS from horizontal
phi.fill(num.deg2rad(-90. - heading))
theta.fill(num.deg2rad(90. - look))
satellite_target = gf.SatelliteTarget(
north_shifts=num.random.uniform(bottom, top, ntargets),
east_shifts=num.random.uniform(left, right, ntargets),
tsnapshot=24.*3600.,
interpolation='nearest_neighbor',
phi=phi,
theta=theta,
store_id=store_id)
# We combine the two sources here
patches = [strikeslip, thrust]
sources = CombiSource(subsources=patches)
# The computation is performed by calling process on the engine
result = engine.process(sources, [satellite_target])
def plot_static_los_profile(result, strike, l, w, x0, y0):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.cm as cm
import matplotlib.colors as mcolors
fig, _ = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(8, 4))
# strike,l,w,x0,y0: strike, length, width, x, and y position
# of the profile
strike = num.deg2rad(strike)
# We define the parallel and perpendicular vectors to the profile
s = [num.sin(strike), num.cos(strike)]
n = [num.cos(strike), -num.sin(strike)]
# We define the boundaries of the profile
ypmax, ypmin = l/2, -l/2
xpmax, xpmin = w/2, -w/2
# We define the corners of the profile
xpro, ypro = num.zeros((7)), num.zeros((7))
xpro[:] = x0-w/2*s[0]-l/2*n[0], x0+w/2*s[0]-l/2*n[0], \
x0+w/2*s[0]+l/2*n[0], x0-w/2*s[0]+l/2*n[0], x0-w/2*s[0]-l/2*n[0], \
x0-l/2*n[0], x0+l/2*n[0]
ypro[:] = y0-w/2*s[1]-l/2*n[1], y0+w/2*s[1]-l/2*n[1], \
y0+w/2*s[1]+l/2*n[1], y0-w/2*s[1]+l/2*n[1], y0-w/2*s[1]-l/2*n[1], \
y0-l/2*n[1], y0+l/2*n[1]
# We get the forward model from the engine
N = result.request.targets[0].coords5[:, 2]
E = result.request.targets[0].coords5[:, 3]
result = result.results_list[0][0].result
# We first plot the surface displacements in map view
ax = fig.axes[0]
los = result['displacement.los']
levels = num.linspace(los.min(), los.max(), 50)
cmap = ax.tricontourf(E, N, los, cmap=plt.get_cmap('seismic'),
levels=levels)
for sourcess in patches:
fn, fe = sourcess.outline(cs='xy').T
ax.fill(fe, fn, color=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5), alpha=0.5)
ax.plot(fe[:2], fn[:2], linewidth=2., color='black', alpha=0.5)
# We plot the limits of the profile in map view
ax.plot(xpro[:], ypro[:], color='black', lw=1.)
# plot colorbar
fig.colorbar(cmap, ax=ax, orientation='vertical', aspect=5)
ax.set_title('Map view')
ax.set_aspect('equal')
# We plot displacements in profile
ax = fig.axes[1]
# We compute the perpendicular and parallel components in the profile basis
yp = (E-x0)*n[0]+(N-y0)*n[1]
xp = (E-x0)*s[0]+(N-y0)*s[1]
los = result['displacement.los']
# We select data encompassing the profile
index = num.nonzero(
(xp > xpmax) | (xp < xpmin) | (yp > ypmax) | (yp < ypmin))
ypp, losp = num.delete(yp, index), \
num.delete(los, index)
# We associate the same color scale to the scatter plot
norm = mcolors.Normalize(vmin=los.min(), vmax=los.max())
m = cm.ScalarMappable(norm=norm, cmap=plt.get_cmap('seismic'))
facelos = m.to_rgba(losp)
ax.scatter(
ypp, losp,
s=0.3, marker='o', color=facelos, label='LOS displacements')
ax.legend(loc='best')
ax.set_title('Profile')
plt.show()
plot_static_los_profile(result, 110., 18*km, 5*km, 0., 0.)
Creating a custom Source Time Function (STF)¶
Basic example how to create a custom STF class, creating a linearly decreasing ramp excitation.
Download gf_custom_stf.py
from pyrocko.gf import STF
from pyrocko.guts import Float
import numpy as num
class LinearRampSTF(STF):
'''Linearly decreasing ramp from maximum amplitude to zero.'''
duration = Float.T(
default=0.0,
help='baseline of the ramp')
anchor = Float.T(
default=0.0,
help='anchor point with respect to source-time: ('
'-1.0: left -> source duration [0, T] ~ hypocenter time, '
' 0.0: center -> source duration [-T/2, T/2] ~ centroid time, '
'+1.0: right -> source duration [-T, 0] ~ rupture end time)')
def discretize_t(self, deltat, tref):
# method returns discrete times and the respective amplitudes
tmin_stf = tref - self.duration * (self.anchor + 1.) * 0.5
tmax_stf = tref + self.duration * (1. - self.anchor) * 0.5
tmin = round(tmin_stf / deltat) * deltat
tmax = round(tmax_stf / deltat) * deltat
nt = int(round((tmax - tmin) / deltat)) + 1
times = num.linspace(tmin, tmax, nt)
if nt > 1:
amplitudes = num.linspace(1., 0., nt)
amplitudes /= num.sum(amplitudes) # normalise to keep moment
else:
amplitudes = num.ones(1)
return times, amplitudes
def base_key(self):
# method returns STF name and the values
return (self.__class__.__name__, self.duration, self.anchor)